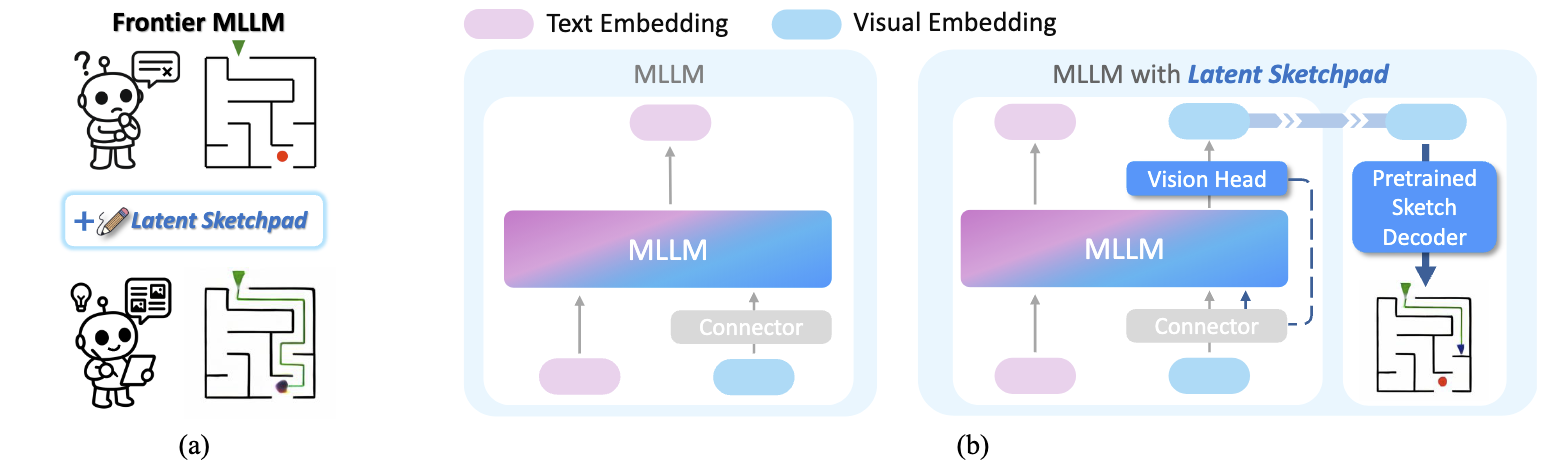
While Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) excel at visual understanding, they often struggle in complex scenarios that require visual planning and imagination. Inspired by how humans use sketching as a form of visual thinking to develop and communicate ideas, we introduce Latent Sketchpad, a framework that equips MLLMs with an internal visual scratchpad. The internal visual representations of MLLMs have traditionally been confined to perceptual understanding. We repurpose them to support generative visual thought without compromising reasoning ability. Building on frontier MLLMs, our approach integrates visual generation directly into their native autoregressive reasoning process. It allows the model to interleave textual reasoning with the generation of visual latents. These latents guide the internal thought process and can be translated into sketch images for interpretability. To realize this, we introduce two components: a Context-Aware Vision Head autoregressively produces visual representations, and a pretrained Sketch Decoder renders these into human-interpretable images. We evaluate the framework on our new dataset MazePlanning, where experiments across various MLLMs show that Latent Sketchpad delivers comparable or even superior reasoning performance. It further generalizes across distinct pretrained backbones, including Gemma3 and Qwen2.5-VL. By extending model's textual reasoning to visual thinking, our framework opens new opportunities for richer human–computer interaction and broader applications in areas such as education and design.
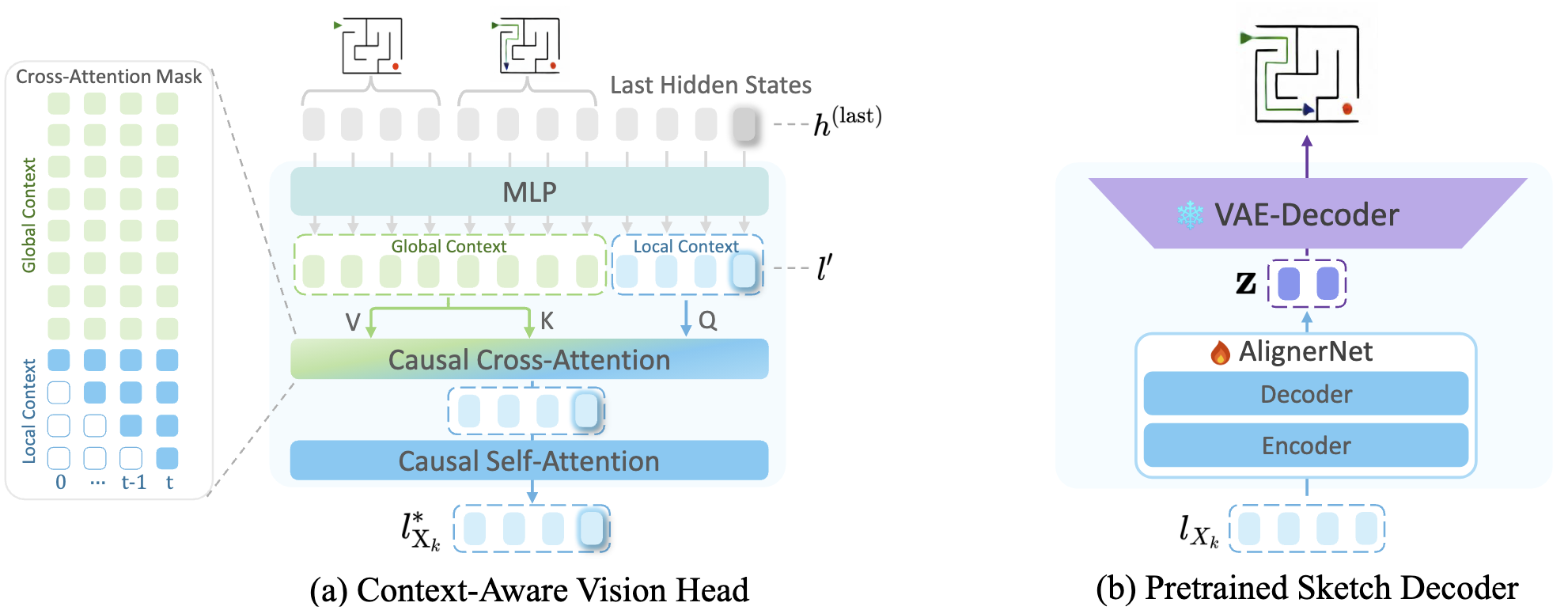
The Vision Head transforms hidden states from the MLLM backbone into visual latents. The Sketch Decoder operates independently, converting these latents into sketch-style images for visualization and interpretability.
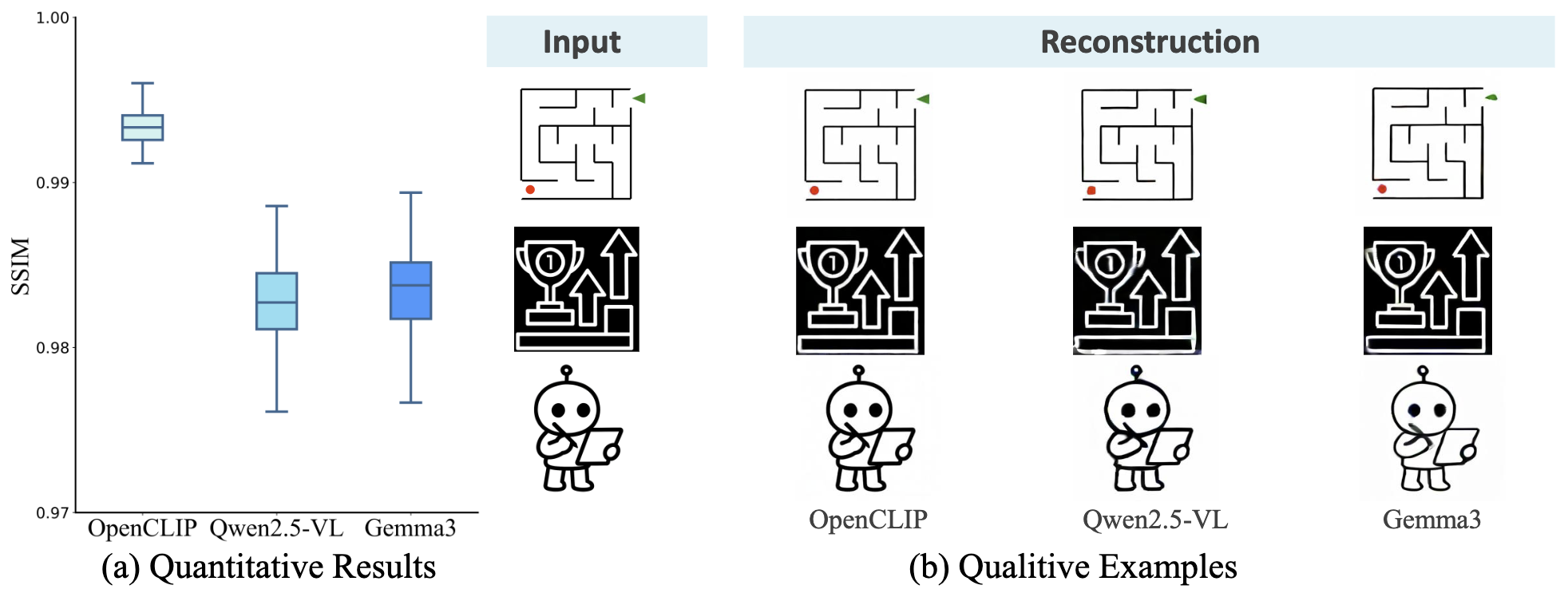
(a) Quantitative reconstruction results (SSIM) across different vision encoders (OpenCLIP, Qwen2.5-VL and Gemma3) on unseen samples from MazePlanning dataset.
(b) Qualitative examples of reconstructed sketches from visual latents produced by each encoder.
@article{zhang2025latentsketchpad,
title={Latent Sketchpad: Sketching Visual Thoughts to Elicit Multimodal Reasoning in MLLMs},
author={Zhang, Huanyu and Wu, Wenshan and Li, Chengzu and Shang, Ning and Xia, Yan and Huang, Yangyu and Zhang, Yifan and Dong, Li and Zhang, Zhang and Wang, Liang and Tan, Tieniu and Wei, Furu},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2510.24514},
year={2025}
}